The 14 most used Islamic financial instruments

What are the most used Islamic financial instruments? This question is the reason for this article. Actually, islamic finance as an alternative to conventional finance offers a number of financial instruments.
However, these instruments must be Sharia compliant. These instruments are more generally classified into three categories. We have financing instruments, participation instruments and non-bank financial instruments. For this article, I present to you the most used financial instruments.
However, if you want to take control of your personal finances in just 6 weeks, I offer you this hyper-efficient guide.

Get 200% Bonus after your first deposit. Use this promo code: argent2035
Let's go
🔰 The Hawala
Un Hawala, is also called the Hundi which means "trust". It is a traditional and informal distributed payment system. Its origins are not very well known. What I can say is that it dates back to the early Middle Ages.
As proof, it can be found in the Fiqh texts of the XNUMXth century. The main role of Hawala is to circulate money in a network of stockbrokers.
However, opinions differ as to the definition of this notion. For some researchers, this system works on the basis of trust and therefore does not require the issuance of a means of payment. As it does not depend on legal enforcement of contracts, this system works even in the absence of a common legal and legal framework.
For others, however, the Hawala is nothing but a bill of exchange, a promissory note, a check or a draft. Technically, the debtor transfers responsibility for paying his debt to a third party who is himself his debtor. Responsibility for payment thus ultimately lies with a third party.
Hawala is a mechanism that allows the settlement of international accounts by accounting transfers. It removes to a large extent the need for a cash transferes. You can comment on this discrepancy in the comments.
🔰 The Mousawama
It's a sales contract classic similar to Murabaha. In this type of contract, the buyer does not know the profit margin applied by the seller.
In other words, the seller is not obliged to disclose the price paid to create or obtain the good or service. This type of contract occurs when it is difficult to determine the cost of a good or service.
Le Mousawama contract presents the same advantages and the same disadvantages than Murabaha. With the evolution of the market, we can already benefit from e-mousawama cards. In fact, the e-Mousawama card is the new concept of Sharia-compliant electronic deposit cards.
This credit card is the only one of its kind that violates the definition of Islamic financing and improves the payment method. The customer gets credit approval and purchases can be made at defined merchants that cover most of your needs.
🔰 The Qard Hasan
Le Qard Hassan is a loan contract between two parties on the basis of social protection. It can also meet a short-term need of the borrower. It's a loan without interest or profit. It is more like aid than commercial credit.
This technique is rarely used by commercial establishments. On the other hand, it can be used in specific situations (in the event of difficulties for an individual or a company, or when one wishes to promote the development of emerging sectors).
In modern terms, many compare this to a payday loan. During the loan process, the repayment amount must be the same as the borrowed amount. This means no interest or riba should only be applied to the loan.
However, in terms of good faith, the borrower may pay the lessor more money in the future. Only it cannot be discussed or agreed upon during the contract.
This means that if they give the lessor a bonus or additional payment, it is permitted, but discussion of such an arrangement is prohibited. This is often done as a measure of good faith and as a way of thanking the lessor.
Qard Hasan is also called a benevolent loan. However, here is my book that tells you everything you need to know about Islamic banks.
🔰 The Mokayada
It is a contract of exchange of a quantity x of a raw material against a quantity y of another raw material not including any exchange of money. The quantities are fixed on the basis of the market prices of the commodities traded
🔰 The kafalah
In Islamic law, the kafala is a specific adoption procedure which corresponds to guardianship without filiation. It also designates the sponsorship prior to the hiring of foreign workers in the Persian Gulf countries.
In Islamic finance the Kafala is a warranty contract whereby a third party guarantees the debt of an indebted agent. Responsibility for the debt vis-à-vis the creditor thus rests with the two parties to the contract.
It is also used as one of the contracts to complement various primary Islamic financial products. Primarily for risk mitigation purposes, such as contracts Musyarakah, Mudarabah, Murabahah, Istisna´, Ijarah and Tawarruq. As with the Hawala contract, the Kafala does not generate any costs beyond the administrative costs.
🔰 The Rahn
Le Rahn is a contract by which an agent secures a debt via collateral (pledge). This type of contract aims to mitigate the counterparty risk borne by the creditor.
The advantage of this contract is that it allows the agent to present an asset in his possession as collateral while retaining its use and ownership. Usually, the guarantee is requested by the creditor from the debtor at the beginning of the contract to avoid default of the debtor not to pay the debt.
The legality of Rahn's concept was mentioned in the Quran in al Baqarah verse 283 “And if you are traveling and cannot find a scribe, then a security deposit (should be) taken. This verse validates the permission to obtain a loan or financing with collateral in Islam.
This was also supported by the practice of the Prophet from a hadith narrated by Aishah (RA): “Rasulullah bought food on credit from a Jew and gave his steel armor as collateral to the seller. » (Saheeh al-Bukhari).
In the current practice of Islamic banking, Rahn's concept can be applied in two different cases.

Get 200% Bonus after your first deposit. Use this official Promo code: argent2035
✔️ The first case is to use the collateral asset or Marhun as pure security.
For example, in housing finance, the bank normally provides the finance facility for the customer to buy the house which makes the bank the creditor and the customer as the debtor, because the finance is a sale on credit which creates the debt.
In this situation, the creditor will make the financed house the Marhun (collateral) to secure its payment obligations to the bank. During the term of the guarantee, the debtor (client) is not able to sell the house to another party unless the bank authorizes him as a creditor.
If the customer fails to settle his debt with the bank, the bank has the power to sell the house to settle the unpaid amount of the sale.
The bank can only take what is owed to the bank and the surplus from the sale (if any) will be returned to the customer. This example essentially paints the picture of Rahn's first application, that is, as pure security.
✔️ In the second case, the al-rahn will be an instrument to facilitate microfinance.
Here, the amount of finance given will depend on the value of the Marhun (pledge of asset). In normal al-rahn microfinance, the client pledges their valuable assets such as gold to the pawnbroker or known as “ kedai pajak gadai islam like the Marhun.
The Marhun will be valued and the customer will be given a loan based on a certain percentage, say 70% of the value of Marhun.
During the borrowing period, the pawnbroker, as the holder of the asset, charges a fee based on daily or monthly calculations for its duty custody of the pledged item until it is retrieved and the debt is settled.
By this, the practice of Rahn as an instrument to facilitate financing can be seen especially in obtaining Micro-financing.
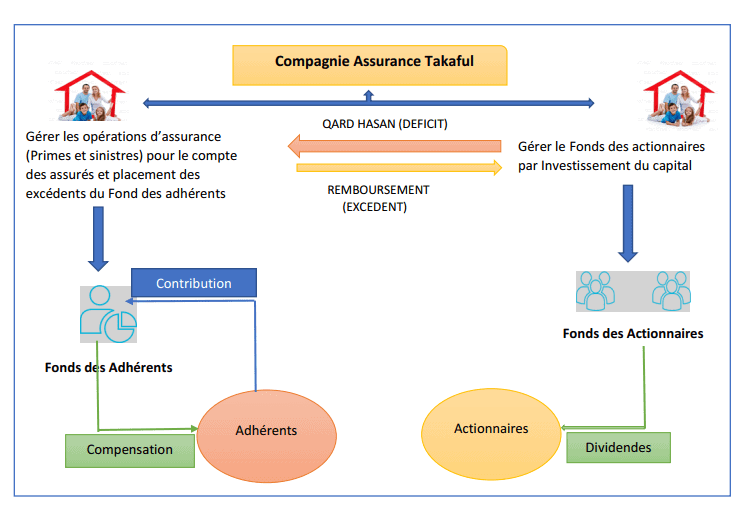
🔰 The Takaful
Le Takaful originated in ancient Arab tribes as a common liability that required those who had committed offenses against members of another tribe to pay compensation to the victims or their heirs.
This principle later spread to many areas, including maritime commerce, in which participants contributed to a fund intended to cover all members of a group who suffered accidents while traveling at sea.
Today it has become a widely used concept in Islamic finance. Takaful is commonly called Islamic insurance. This is due to the apparent similarity between the contract of Kafalah (guarantee) and that of insurance.
It is based on principles of mutuality and cooperation, encompassing the elements of shared responsibility, joint indemnity, of common interest and solidarity.
Islamic insurance requires each participant to contribute to a fund which is used to support each other. Each participant contributes amounts sufficient to cover expected claims.
???? The different shapes byislamic insurance
Like the Sukuks, there are several forms of Takaful. Private halal offers financial coverage in all areas of daily life. Whether you are an individual or a business.
✔️ Non-profit Takaful
They signify that the activity is managed on a purely mutual or cooperative basis. This regardless of their legal forms. For this type of Takaful, a management committee is often set up by the program participants.
The Board manages the activity on behalf of all policyholders. There is therefore no separate entity in charge of managing the activity as in the following case.
✔️ For-profit Takaful
They are said to be for profit if the management of the fund is entrusted to a commercial entity (operator Takaful). It is not a committee as in the previous case.
Depending on the rules specific to each jurisdiction, the fund may be integrated with the operator. Only, there must be a clear separation between the funds of the shareholders and those of the participants in the insurance program.
In some countries, a program Takaful can be offered by a "window" of a traditional insurer. This is the case in several African countries such as Cameroon, Senegal, Morocco and many others.
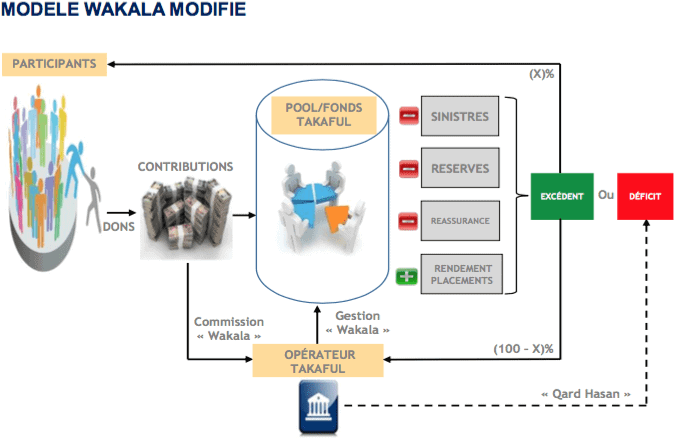
🌲The different models Takaful
There are several ways to establish Takaful insurance contracts. But I only present to you the most used models.
Models inspired by Mudaraba, models inspired by wakala, hybrid models and models inspired by donations (Waqf).
✔️ The model Mudaraba pure
In a Takaful Mudaraba model, we have a Mudarib (the entrepreneur) who plays the role of the Takaful operator and the rab ul mal (capital providers) who the participants.
The contract specifies how the gains generated by the placement and/or the surpluses of the operation Takaful will be distributed between the operator Takaful and attendees.
Losses are the sole responsibility of the participants as contributors of capital. Except in the event that the operator is found to have committed professional misconduct or been negligent. In this case the Mudarib or the entrepreneur is not compensated for his efforts.
✔️ The model wakala pure
This model is modeled on the agency relationship (principal–agent). It is used for subscription and placement. In the subscription, the operator Takaful acts as agent for the participants to manage the fund Takaful.
All risk is borne by the fund and any operating surplus belongs to the participants. The operator Takaful does not participate directly in the risk borne by the fund or in any surplus/deficit of the fund.
On the other hand, the insurer Takaful receives a commission wakala fixed which generally represents a percentage of the contributions paid. These fees compensate his service as manager.
The operator's remuneration may also include a performance fee, deducted from any surplus. It is a motivating measure for effective management of funds.
✔️The hybrid model: combination wakala et mudaraba
In this model, two sub-contracts are formulated. First the W contractmind adopted for the subscription, and then the contract Mudaraba used for fund investments.
This model is the most recommended by international organizations. In practice, it is widely adopted by insurers Takaful.
✔️ The Waqf model
In the sense of the Muslim religion, the waqf is a kind of donation made by an individual in perpetuity. With this model, the insurer first makes a donation. Subsequently, policyholders make additional contributions to be used to settle claims.
The operator receives a fixed subscription commission. Insured parties receive the balance of funds after settlement of claims. This model is mainly present in Pakistan.
In all of the above models, the insurer will typically provide an interest-free loan to cover any default in the fund. takaful. THE loan is repaid using surpluses future of the fund takaful. The following table presents the difference between classical insurance and Islamic insurance, the takaful.
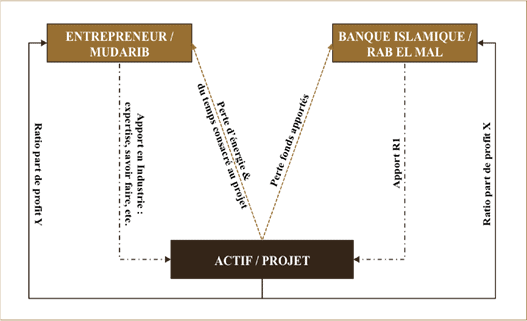
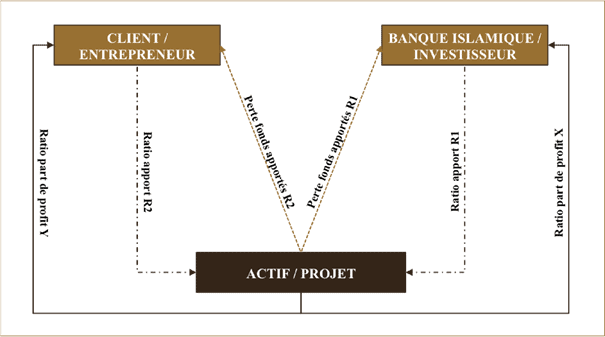
🔰 The Mudharaba
Le Mudharaba reference to a commercial contract in which one party contributes capital and the other a personal effort. The proportional share of profits is determined by mutual agreement.
But the loss, if any, is borne only by the owner of the capital, in which case the entrepreneur gets nothing for his labor. The financier is known as " rabal maal » and the entrepreneur under the name of « mudarib ».
As a financing technique adopted by Islamic banks, it is a contract in which all the capital is provided by the Islamic bank while the business is managed by the other party.
Profit is shared according to previously agreed ratios and loss, if any, unless caused by negligence or breach of contract terms by the " mudarib » is supported by the Islamic bank.
🔰 Musharakah or Musharakah
The origins of the word Musharakah originate from Arabic Sharikah which means partnership. For Islamic jurists, the legality and permissibility of Musharakah is based on the provisions of the Quran, Sunnah and the Ijmah (consensus) of the scholars.
In Islamic finance, the Musharaka is a method of financing which is in the form of a partnership. It is a contract signed between the bank and its client in which each party contributes capital in equal or varying degrees either to establish a new project or to participate in an existing project.
The profits or losses generated are distributed in accordance with the contractual clauses. They are shared in accordance with the Musharakah agreement. Losses are normally shared in proportion to the capital contributed by each Musharik.
Musharakah contracts can take the following forms: the constant and decreasing Musharakah. A Musharakah agreement can be entered into for a short or long term period. The capital contributed by the bank in a Musharaka can remain constant throughout the contractual period.
???? Types of contracts musharakah
Like many Islamic financial products, there are two types of le musharakah : the musharakah final and the musharakah degressive.
✔️ The definitive musharakah
This version of the contract musharakah allows the bank to participate in the financing of the project in a sustainable way and to benefit from the dividends in its capacity as co-owner partner. In this case, the bank is dealing with a medium or long-term use of these stable resources.
The bank's contribution can take the form of equity participation in existing companies. This contribution can take the form of a contribution to the increase of the share capital in the new companies.
This type of musharakah with equity securities meet in traditional finance to secure significant control in an existing business. In this contract there is no repayment of capital.
✔️ Le musharakah decreasing
With musharakah decreasing the bank is gradually withdrawing from the company's capital. The customer will pay, at regular intervals, to the bank the part of the profits due to him as he can reserve part or all of his own share to reimburse the capital contribution of the bank.
After recovering all of its capital and accrued profits, the bank withdraws from the project or operation. This formula is similar to investment securities in conventional finance.
???? The advantages of financing musharakah
Funding by musharakah has several advantages for the bank and the co-partner(s). For the bank, this formula offers long- and/or medium-term investment opportunities for its resources.
It constitutes a source of regular and consistent income likely to enable the bank to provide its depositors and shareholders with an attractive rate of return.
For clients or co-partners, the musharakah is presented as a form of long and medium term credit. As such, it constitutes the most effective method of financing more suited to the needs of creative cycles and business development, both in terms of building up and/or increasing capital and acquiring and/or renovating equipment.
Le musharakah is highly sought after by promoters for the creation of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The contribution of each party must be available at the time of the completion of the operation, subject of the financing.
However, Islamic law allows the moucharaka in transactions benefiting from deferred payment, provided that each of the parties assumes part of the commitment vis-à-vis the supplier(s) (charikat wudjouh).
In this case, the role of the bank generally consists of issuing bank guarantees (endorsement, documentary credit, letter of guarantee, market guarantee, etc.). Any agreement aimed at guaranteeing one of the parties the recovery of its assistance regardless of the results of the operation is null and void.
In this regard, the bank has no right to claim reimbursement of its contribution. Except in the event of a violation of the contractual clauses, gross negligence in the management of the case or breach of trust.
The bank may require its partner to provide guarantees, but it may only enforce them in one of the cases mentioned above.
🌲Problems related to the practice of musharakah
In practice, the use of this method of financing remains low because of the high credit risk. Credit risk related to financing musharakah is the probability of non-recovery funds advanced in volume and in a timely manner. The high level of this risk finds an explanation in:
- Labsence of guarantees ;
- A high rate of moral hazard and adverse selection;
- A lack of qualified staff at the level of the banks in terms of technical evaluation of projects;
Alongside this credit risk, contracts of the type musharakah are also subject to equity risk, the assets held in equity by the investor may depreciate. In the contract musharakah all parties participate in the capital and therefore in any losses.
To le musharakah declining, one of the parties undertakes to repurchase all the capital in shares at a predetermined price.
This is exposed to an additional risk while the other parties do not suffer losses (forward sale). Finally, the capital risk is also inherent in this type of contract in the event of financial losses.
🔰 The Ijara or Ijarah
The term Ijara comes from the Arabic " air which means reward or salary for work done or services rendered. In the financial world, it is a bilateral contract involving the transfer of the use of an asset for an agreed period for a consideration.
It involves two parts: the lessor or Muajir and the tenant or Mustajir the asset. The owner of the object temporarily transfers his usufruct to the tenant for the agreed period and the tenant must be able to benefit from it without consuming it.
Ownership of the leased property belongs to the lessor, as well as all risks related to ownership. Physical possession of the property is held in trust by the lessee. He is not responsible for any loss, destruction or reduction in value of the property.
The rules of ijara, in the sense of leasing, are very analogous to the rules of the sale. The only difference between ijarah and sale is that in sale, the corpus of the property is transferred to the buyer. In ijarah, the corpus of the property remains the property of the transferor, but only its usufruct is transferred to the lessee.
🌲 Types of Ijara financing contracts
The operation Rent can take one of two forms:
- Ijara Montahia bi tamlik. Ownership of the leased property is transferred to the customer under a separate contract from that of Rent at the end of the contract;
- Ijara Tachghilia or Ijara wa Iktina. This type of contract refers to a simple rental.
However, we can also distinguish two types of operations Ijara Montahia bi-tamlik :
Ltransactions involving movable assets. These are operations relating to capital goods whose acquisition is possible at the end of the contract by the lessee;
Lreal estate transactions. These are transactions by which the institution gives Rent real estate, purchased by him or built on his behalf, when these operations allow the tenant to become the owner of all or part of the leased property at the end of the contract rent
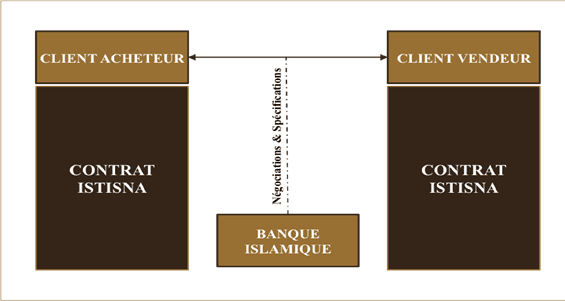
🔰 The Istisna'a or Istisna
Istisna'a is a type of sales transaction where the buyer places an order to the seller to manufacture certain assets and the sale is concluded upon delivery of the asset to the buyer. Istisna is used for provide funding facility for transactions where the customer is involved in manufacturing or construction.
In the context of the Istisna financing transaction, the client manufactures goods for the Bank and upon delivery of the goods to the Bank, the client is appointed as the Bank's Agent to sell these goods on the market.
As an advantage, the Istisna can be used by small, medium-sized commercial enterprises and legal persons. Otherwise, it is an ideal mode for short-term financing because it makes it possible to respect the financial balance. The customer can also use it to meet their working capital needs.
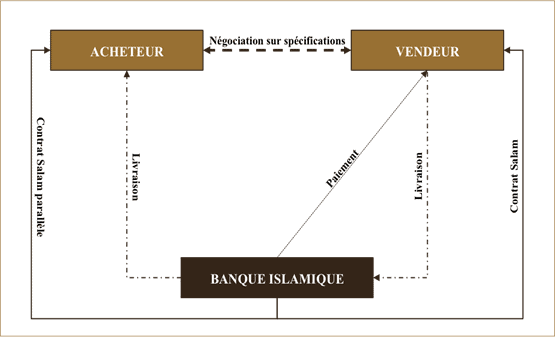
🔰 Salam
Salam is a contract of sale whereby the seller agrees to supply specific goods to the buyer at a later date in exchange for an advance price paid in full in cash.
It's a kind of reverse credit sale. This contract creates a moral obligation for the seller of Salam to deliver the goods. Salam contract cannot be terminated once signed. According to Sharia a commodity (intended to be sold) must be in the physical or implicit possession of the seller.
However, there are two exceptions to this general principle in Sharia. One is Salam and the other is Istisna'a. Both are sales of a particular nature. Salam is used to finance similar agricultural products. The Istisna'a is used to finance similar manufactured products.
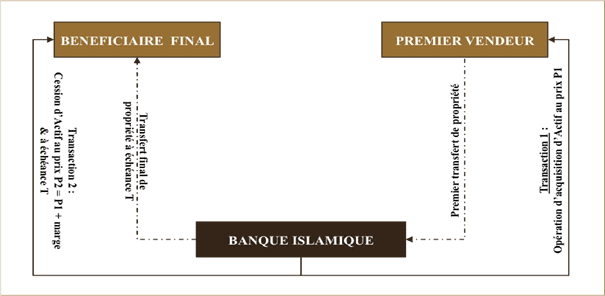
🔰 The Murabaha
Le murabaha is an Islamic financing structure that works like a sales contract. The Murabaha, also called cost plus financing, a customer asks a bank to purchase an item on their behalf. In this contract, the seller and buyer agree on the cost and profit margin of an asset.
In practice, the bank makes the purchase and makes the deal with the customer's seller of choice and then makes a sale with the customer on Murabaha basis. Later, the customer reimburses the bank according to the terms of predefined installments or settlement.
???? The operating principles of the murabaha
Le murabahah as practiced by Islamic banks is a forward sale transaction. The cost price, the profit margin and the payment period(s) must be known beforehand and accepted by the parties.
In case of delay in the payment of the installments, the bank can apply to the defaulting customer late penalties which will be lodged in a special account. But at no time can the bank revise its profit margin upwards in return for the overrun.
In the event of bad faith on the part of the customer, the bank is entitled to claim, in addition to the penalties, compensation for unhonoured deadlines. In which case, the damage should be assessed against objective criteria specific to the bank. This assessment should not involve interests.
After completion of the contract murabahah, the merchandise becomes exclusive and definitive property of the final buyer. It will remain, whatever the incidents that may occur subsequently. However, the bank may take a pledge on the goods sold as security for payment of the sale price.
???? The problems related to murabaha
The points of view are different on this promise to purchase if it constitutes an obligation or not. The promise to purchase is an obligation vis-à-vis the customer. Jurisconsults believe that the obligation should not apply to the client.
The customer should be able to request the cancellation of the contract even after having given the order and paid. The most significant counterparty risk linked to the murabaha emanates from this diversity of apprehension of the legal nature of the contract.
Dsecond problem of murabaha lies at the level where the counterparty fails to meet the deadlines. This late payment can cause losses for the bank. On the market, the rate of return risk arises if the rate of return of the operation is different from the current reference rate; then there is the possibility of financial losses.
To manage the counterparty risks related to the contract of murabaha, the upfront payment of a large commission has become common practice.
🔰 The sukuk
Commonly known by their Arabic name, sukuk, and often mistakenly referred to as “islamic bonds“, Shariah-compliant fixed income capital market instruments have steadily increased their share of global markets over the past decade.
Initially developed exclusively in Muslim-majority jurisdictions, the global Sukuk market has seen considerable development over the 10 last years, with a number of high-profile corporate issues and a number of sovereigns tapping the market.
Sukuks are financial products whose terms and structures are compliant with Sharia, with the intention of creating returns similar to those of conventional fixed income instruments such as bonds.
???? What are the forms of Sukuks?
Like most Islamic financial products, Sukuks can take many forms. Thus, there are approximately ten forms of Sukuk.
✔️ Zero-Coupon Sukuks
The first type of Sukuk is the zero-coupon Sukuk. In practice, it is a broadcast of sukuk in which the assets to be mobilized do not yet exist.
This issuance may also concern assets that are not created at the time of their issuance. The funds mobilized through the Slaw will be used to create more assets on the company's balance sheet.
Finally, we can say that zero-coupon Sukuks are similar to "certificates murabaha et Istisna'a ". They are therefore not merchants on the secondary market.
✔️ Sukuk Al-Ijara (Lease Agreement)
The second type of Sukuk is Ijara type. As a reminder, the Ijara is a kind of leasing that we encounter in traditional finance. Consult our article on the Ijara.
This is very often used. This solicitation can be explained by the simplicity of the structure of these sukuks. Moreover, some researchers describe it as the structure of sukuk classic from which all the other structures of sukuk have been developed.
✔️ Sukuk Al-Istisna
The third form of Sukuk is the Sukuk al-Istisna'a. It is a form of sukuk derived fromexceptional , promising is a lease. This form is appropriate for financing new development projects.
However, some structural drawbacks have proven difficult to overcome. For this, it does not present itself as an alternative source of Islamic multi-source project financing in the manner once predicted.
✔️ Sukuk Al Murabaha
The fourth form of Sukuk is Sukuk Al-Murabaha. Unlike the other forms, this form is used less.
The term " murabaha is widely understood to refer to a contractual agreement between a financier (the seller) and a customer (the buyer) whereby the financier would sell specific assets or products to the customer for cash delivery pending that the customer would be able to meet its deferred payment obligations in accordance with the agreement " murabaha ». Thus, it is this logic that animates the Sukuk Al-Murabaha.
✔️ Hybrid Sukuk
The fifth form of Sukuk is what has been called hybrid Sukuks. They are Sukuks at a hybrid rate based on an association of assets.
It is a type of Sukuk in which the underlying pool of assets consists of two or more Islamic finance contracts. In other words, this type of Sukuk requires several subcontracts.
✔️ Sukuk Al-Musharaka
The sixth form of sukuk is Sukuk Al-Musharaka. The popularity of this structure has declined in recent times, since the declaration of the AAOIFI in 2008.
The AAIOIFI had criticized the use of purchase commitments in structure sukuk al-musharaka. In fact, the term musharakah is derived from the word " Companies meaning "partnership".
In its simplest form, an arrangement musharakah is a partnership agreement where each partner contributes part of the capital to carry out a project. This contribution may be in kind or in cash.
✔️ Sukuk Al Salam
The seventh form of Sukuk is Sukuk Al-Salam. In fact, the Salam is a reverse credit sale contract where the buyer pays today and receives the asset later. Thus the Sukuks al-Salam will relate to assets in the process of production or manufacture.
From a Sharia point of view, for a sale to be valid, the object of the sale must exist. The seller must own it, the asset must be real. Exceptions to this general position are sales made under "S" contractsalam " and " Exceptional ».
✔️ Sukuk Al-Wakala (agency contract)
The eighth form is the Sukuk Al-Wakala. The concept " wakala literally refers to an arrangement by which one party delegates some of its responsibilities to another party to act on its behalf.
Un wakala is therefore a kind of agency relationship in classic finance. A structure of sukuk al wakala is inspired by the relationship.
✔️ Sukuk Al Mudaraba
The ninth form is Sukuk Al-Mudaraba. By structuring a program sukuk, the first step is often to analyze exactly what an originator's business entails and what assets (if any) are available to support the issuance of sukuk.
✔️ Sukuk Al Mudaraba
The last form is the Sukuk Al-Mudaraba. It is literally called " sukuk investment ”. These are certificates sukuk » of equal value that are issued and sold to investors
Leave me a comment



















I am interested in Islamic finance but in my country there is none
I understand you, what country are you in?