The particularities of Islamic banks

The particularities of Islamic banks are numerous. While the conventional banking system is based on lending with interest, Islamic banks are based on very different principles dictated by Islamic law (Sharia). These principles introduce many specific features into the operation and services offered by this type of banking institution.
With the rise of Islamic finance in recent years, banks that respect the precepts of Islam arouse growing interest, both in Muslim countries and in Western financial centres. Their outstandings today exceed 1500 trillion dollars worldwide !
Thanks to this article, no more secrets for you on what Islamic banks are and how they differ from traditional banking establishments. You will know exactly how they operate and what specific services they offer to their customers.

Get 200% Bonus after your first deposit. Use this promo code: argent2035
Ready to know everything about the workings of this alternative banking system? But before you start, here is a protocol that allows you to build your first internet business.
???? What is an Islamic bank?
Islamic banking is any bank that is committed to applying the principles of Sharia law in its banking transactions.
It is also defined as a financial institution whose main task is to attract monetary funds and to use them efficiently so as to guarantee their increase in accordance with sharia rules.
This definition mentions the essential elements that Islamic banks (IB) are bound to respect. It is about adhering to recognized Sharia standards, whether in production, distribution, consumption or savings activities within an entire economic system.
Hence, BI can be defined as a bank with specific legal characteristics that offers various Sharia-compliant services to its customers. This definition highlights the characteristics of an Islamic bank.
The characteristics of an Islamic bank
Unlike conventional banks (BC), Islamic banks arebanks authorized to carry out a professional activity. They are authorized to carry out their activities in the same way as their conventional equivalents. Regardless of the regulations in force in each country where they are established.
They offer services and maintain banking relationships with their customers in accordance with the Islamic Sharia standards. BIs must avoid certain practices such as wear and tear (riba), speculation and uncertainty.
The difference lies in the use of funds which must be in accordance with Sharia law and based on contemporary Islamic jurisprudence.
IBs act as mediators between lenders and people who want to borrow money. We can therefore say that the services offered by the BIs are similar to those offered by the BCs insofar as the objectives are the same, to satisfy a clientele.
If in classical finance the rule that governs the decisions of an economic agent is the maximization of profit, profitability is not the only objective Islamic operators. The following image shows you the difference between a traditional bank and an Islamic bank.
BI favors investments in tangible assets, shares profits and losses fairly with its partners and advocates the crowdfunding of projects.
(I.e. Classification of Islamic Financial Institutions
Islamic financial institutions can be classified according to several criteria. Depending on their activities, their locations or whether or not their financial activities are entirely Islamic.
✔️ Classification according to the nature of the activities
Depending on their activities, a distinction is made between insurance companies, Mudharaba, Islamic microfinance institutions and Islamic banks.
BIs can be either commercial or retail banks, or investment or merchant banks. Deposit banks are those whose main activity is to carry out credit transactions and to receive demand and time deposits from the public.
Are called investment banks, those whose activities consist in granting loans with a duration of more than two years. Merchant banks, on the other hand, are those whose main activity is, in addition to the granting of loans, the acquisition and management of holdings.
✔️ Classification according to location
Depending on their locations, we distinguish banks which operate in countries entirely “ Islamized » and those that operate in non-Muslim countries.
In the first case, banks are governed by a single regulation. In the second case, they are subject to dual financial regulations (Islamic and conventional) that are more or less compatible.
✔️ Classification according to whether their financial activities are Islamic or not
According to this criterion, a distinction is made between fully Islamic banks and those with only Islamic counters or windows. However, the legality of these Islamic windows is not unanimously recognized. There is a real risk of mixing licit and illicit flows (not in accordance with Islamic law).
???? The risks inherent in the activity of Islamic banks
In addition to the above-mentioned risks, there are risks unique to Islamic banks. They are related to the nature of the activities and the culture ofIslamic banks.
In addition, the 3P principle generates additional risks such as displaced commercial risks, fiduciary risk, reputational risk, entanglement risk, legal risk and even religious risk.
🔰 Displaced or shifted commercial risk
Le misplaced commercial risk, very important, comes from participatory investment accounts which require the sharing of profits and losses between the bank and the holders of these accounts.
This risk is due to a transfer of risk associated with deposits to the bank's shareholders. Sometimes, shareholders find themselves forced to give up part of their profits to remunerate depositors. This is with a view to preventing massive withdrawals caused by low rates of return.
If in theory the profits are shared in pre-agreement ratio and the losses on the assets are at the responsibility of account holders, in practice the principle of sharing real profits with investment account holders is far from being the common practice of Islamic banks.
Sometimes the bank finds itself unable to pay a rate of return equivalent to the return distributed by other banks. This sometimes pushes depositors to withdraw their money and deposit it in another bank that can offer them a significantly better return.
Therefore, BI must either manipulate the rate of return or reduce the share of profits going to shareholders.

Get 200% Bonus after your first deposit. Use this official Promo code: argent2035
🔰 The entanglement of credit risk and market risk
The number of parties involved in transactions simultaneously exposes the bank to credit risk and market risk. THE risk of "entanglement" is related to the fact that many Islamic transactions are three-way.
The example of the contract murabaha illustrates well the characteristic of risk transformation. Indeed, to finance a customer by murabaha, the BI must first acquire the asset and then resell it to the client. Doing so, she transfers ownership of the asset from the bank to the buyer of the asset.
The risk to which the bank is exposed is transformed from market risk following the holding of a physical asset on the date of acquisition to credit risk at the time of the resale of the asset to the customer. We then speak of the entanglement of credit risk and market risk.
🔰 Reputation risk
In the logic of competing with CBs, BIs tend to favor products that are similar to those of the CB. It is observed that BIs most often use sales contracts and not participatory contracts. THE reputational risk should therefore be taken seriously.
It can extend beyond banking itself and disrupt the Islamic finance industry. Worse still, the image of the bank would be extremely difficult to restore, even after several years.
Market confidence is therefore of paramount importance for the development of this finance, which aims to be participatory and " Fair ».
🔰 Fiduciary risk
Once its reputation is lost, BIs will face another risk called fiduciary risk. This is the risk that customers will lose confidence in their bank following non-compliance of banking operations. This is what damages the bank's image and leads to a loss of confidence.
🔰 The legal risk
This is the risk of litigation with a co-contractor due to inaccuracies in the contractual clauses. This risk can also be linked to legal loopholes, ambiguities or inappropriateness of legislative and regulatory texts.
This risk may be linked to the failure of legal services. Their occurrence is likely to result in direct or indirect financial losses for BI.
????Islamic banking risk management
The mode of operation of participatory investment accounts makes BIs the most exposed to maturity risk. Have developed commercial capacities for financing and investment which allow them to increase the maturity of their assets.
Even if it remains essentially short term. This process increases maturity gaps and poses serious asset-liability management issues. As Islamic banking risks, we have displaced risk, fiduciary risk, reputational risk, religious risk, etc.
🔰 Ldisplaced or shifted commercial risks
As we presented above, the displaced commercial risk is the worst in BI. It results from the volatility of returns on assets financed by funds deposited in participatory investment accounts.
This risk manifests itself when the real rate of return is lower than the returns expected by account holders. To deal with this type of risk, banks very often develop appropriate management methods.
As a result, they can engage in a set of practices that smooth the rates of return on investment accounts so as to offer holders of these accounts a rate of return comparable to the rate of return in other banks. .
These techniques for smoothing rates of return are mainly based on the transfer of income in favor of the holders of investment accounts and the setting up of reserves.
The BI can vary the profit sharing ratio as well as its remuneration as Mudarib. Indeed, the share of the profits of the bank determined initially is the maximum share. While the share actually distributed varies from one period to another depending on the real rate of return.
BI could reduce or even drop its commission for Mudarib below the contracted part. For this, it will temporarily allocate small profits or larger losses to shareholders. And this for the benefit of investment account holders.
In addition, banks can proceed with the mobilization of funds from shareholders by placing these funds at a considerable level. This in accordance with Basel II and III requirements.
🔰 Reputation risk management
Reputational risks are difficult to identify, pin down, quantify and therefore reduce. These risks are inherent human behavior and activity. In the same way, the risks sometimes of one-upmanship, sometimes of religious laxity are inherent in human choices.
BIs will only be able to protect themselves from this by promoting a degree high integrity and ethics, declined down to the most individual level. In fact, Islamic banks suffer from a lack of professionals sufficiently experienced in Islamic finance.
To reduce this type of risk, staff training or retraining and innovation are key links. Otherwise, IBs must carry out perception studies in order to quantify this type of risk. Doing so, BI could simultaneously reduce operational and fiduciary risks which are also linked to human activity.
Islamic banking governance
Management Islamic banking has a particularity. The leaders of Islamic banks are independent and have absolute freedom in making investment decisions. To this end, CIP holders incur significant risks and have limited pressure mechanisms.
However, it is difficult to directly observe the behavior of the bank or to access certain information. To deal with this problem, the most effective mechanism seems to be the remuneration of the bank as manager.
This remuneration depends directly on the return on the assets financed by the participatory investment accounts. Conflicts also exist between leaders and the c advisory boardwould do. Because the power of this committee is limited.
Such precision in the annual reports gives a clear idea of the balance of power that exists between the advisory committee and the head of the institution.
🌿 Islamic banking governance mechanisms
By definition, a mechanism is an assembly of mechanical parts, some of which can move relative to others.
This assembly does not therefore constitute a solid. A governance mechanism is an independent body whose role is to reduce the perverse effects of the agency relationship. Bank governance is distinguished by the importance of mechanisms, both external and internal.
In Islamic banks, another component, the religious component (the Sharia committee for example), is added to these mechanisms.
✔️ Religious banking regulation
One of the particularities of Islamic banking governance lies at the level of regulation. There banking regulation is the primary mechanism of Islamic banking governance.
It is the fact of supervising and controlling the banking activity, by subjecting it to compliance with the various standards. Its objective is to control risks and preserve the security of depositors and the stability of the financial system.
In Islamic banks, regulation emanates from the standards enacted by the AAIOIFI and from international regulations, the Basel Committee.
The role played by regulation in BI is the same in BC. However, to this role is added the religious dimension of regulation, which ensures that operations comply with Islamic law. It seeks to ensure that banks faithfully fulfill the conditions established by Sharia.
✔️ The Board of Directors
Le board of directors is the supreme body in Islamic banks. The atypical nature of this board is one of the particularities of bank governance. To access this board, candidates must meet certain conditions.
(a) Be of the Muslim faith
The nature of transactions carried out in Islamic banks requires that board members have sound knowledge of Islamic law. Thus, these members are chosen from among Muslims.
This reflects the concern to preserve trust between the bank and its customers. The presence of a non-Muslim member would put the bank at odds with its principles.
(b) Hold the number of shares required by the articles of association
The members of the Board of Directors must hold a minimum number of shares set by the articles of association.
These shares are nominative, inalienable and serve to guarantee good management on the part of the member of the board of directors. The inalienability of members ends when the administrator ceases to hold office.
(c) Not to have fallen into an incompatibility
This layout is not common to all Islamic banks. Some banks adopt this condition and specify that the member of the board cannot occupy another position in the bank except that of chairman of the board of directors (PCA), or that of general manager (DG).
✔️The Sharia Committee
The presence of a Sharia committee is part of the particularities of Islamic banking governance. The Sharia Council is an independent body of jurists specializing in Islamic commercial jurisprudence.
It is a collegiate body made up of specialists of Islamic law who, upstream, issue legal opinions relating to the conditions of legality of the operations and products offered by the bank and who, downstream, verify the implementation of these opinions.
It meets at the end of each financial year for a religious audit of the bank's financial and investment operations. Its main missions are determined jointly by the AAOIFI and the IFSB. The missions of the sharia council are mainly fivefold:
- Assist financial institutions in the development of contracts and products so that they are in conformity with the principles of Islamic law;
- Certify the acceptability of financial instruments through fatwas;
- Vérifier that the transactions comply with the fatwas issued;
- Vérifier the calculation and settlement of the zakat ;
- Distribute non-Sharia compliant income to charity.
✔️ Designation and composition of members of the Sharia committee
In practice, the designation of the members of the sharia councils is done on the basis of a decision of the board of directors or by deliberation in the general assembly. The regulator generally favors the last option.
According to the standards proposed by the AAOIFI, a sharia council is composed of a minimum number of three (03) members. It must not include among these members a director of the institution or a shareholder with significant influence. The size of this council varies according to the banks and can reach seven (07) members.
✔️ The profile of the members of the Sharia committee
The composition of the councils of sharia is a strategic decision. In fact, the use of a recognized jurisconsult can only strengthen the notoriety and credibility of the bank with its customers.
These jurisconsults have generally followed specialized training in Sharia regulations provided in Islamic universities.
Combining numerous knowledge, ulama or Sharia Scholars are experts in Islamic finance. They are authorized to issue their fatwa on the character halal ou haram of a contract, business, or financial product. These ulama must have theological, financial knowledge, and a perfect mastery of fiqh.
✔️ Mode of operation of Sharia committees
In a sharia committee, there is a president and possibly a vice. The board may delegate part of its powers to an executive committee which ensures a more regular presence. This sharia council can refer the matter to the board of directors in the event of disagreement on this point. This committee reviews the day-to-day operations of the bank and ensures Shariah compliance.
Finally, we can say that the particularities of Islamic banking governance lie in the functioning of new bodies such as the Sharia committee.
💰 Islamic investment and deposit accounts
Regarding the collection of deposits, Islamic banks offer two compliant formulas:
Mudaraba investment accounts
Mudaraba investment accounts are a form of Islamic account that allows investors to share in the profits and losses of an investment project. In this type of account, an investor provides the funds needed for an entrepreneur to complete a project, while the entrepreneur provides his or her expertise and labor.
The profits generated by the project are shared between the investor and the entrepreneur according to a pre-agreed ratio, while the losses are borne solely by the investor.
This allows investors to participate in investment projects consistent with the principles of Islamic finance, which prohibits usurious interest. Mudaraba investment accounts thus offer an ethical alternative that complies with religious principles for Muslim investors.
Musharaka participation accounts
These musharaka participation accounts are another form of Islamic account that allows multiple parties to participate financially in an investment project. In this type of account, investors provide the necessary funds for the project and share both profits and losses according to their respective stake.
Unlike mudaraba investment accounts, investors in musharaka participation accounts also have the opportunity to actively contribute to the management of the project. This favors transparency and accountability mutual between the parties involved.
Musharaka participation accounts offer Muslim investors another option consistent with the principles of Islamic finance, with an emphasis on fair participation and risk sharing.
💳 Suitable banking products and services
To meet current banking needs in compliance with Sharia, Islamic banks offer suitable products:
Current accounts and savings accounts
Checking accounts and savings accounts are two types of bank accounts commonly used by individuals and businesses. These accounts are mainly used to carry out everyday transactions, such as paying bills and making purchases, while savings accounts are used to save money in the long term.
They allow account holders to deposit and withdraw money at any time, without limits on frequency or amount. They also offer services such as checks, debit cards, and bank transfers to make transactions easier.
Savings accounts, on the other hand, are designed to encourage long-term saving. They usually offer a higher interest rate than current accounts, but limit the number of withdrawals and the amounts that can be withdrawn.
Savings accounts may also include features such as certificates of deposit and retirement savings accounts to help customers achieve their long-term financial goals.
Bank cards
Cards are offered with either an entry fee or a fixed annual commission not linked to expenses.
consumer loans
In Islamic banks, consumer loans are structured to respect the principles of Islamic finance, which prohibit usurious interest (riba) and excessive speculation. Instead of charging interest on loans, Islamic banks use financing structures based on Sharia-compliant contracts.
One of the structures commonly used is that of Murabaha. In this case, the bank buys the good desired by the customer and resells it at a premium price, with an installment payment agreed in advance. This allows the customer to acquire the property without having to pay interest, but rather by paying a higher price over a specific period.
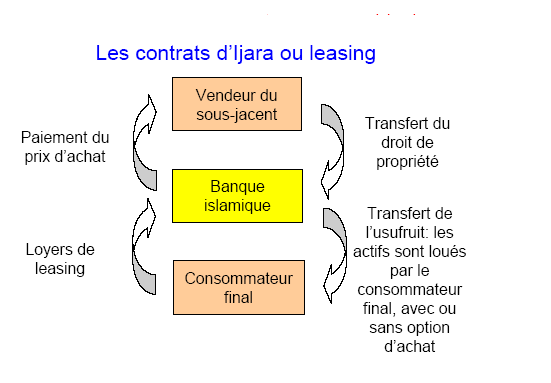
Another structure used is that of the Ijara, which is similar to a rental with purchase option. The bank buys the property and rents it to the customer for a fixed period, with regular payments. At the end of the contract, the customer can buy the good at an agreed price or return it to the bank.
Mortgages
Real estate loans are loans granted by banks and financial institutions for the purchase or construction of real estate, such as a house or apartment. These loans allow borrowers to finance the acquisition of real estate while repaying the amount borrowed with interest over a specified period.
In the context of Islamic banks, real estate loans are structured to respect the principles of Islamic finance. Islamic banks use different Sharia-compliant financing structures to offer usurious interest-free (riba) alternatives to borrowers.
One of the commonly used structures is that of the Murabaha. In this case, the bank buys the real estate desired by the borrower and resells it at a premium price, with an installment payment agreed in advance. This allows the borrower to acquire the property without having to pay interest, but rather by paying a higher price over a fixed period.
Another structure used is that of the Ijara, which is similar to a rental with option to buy. The bank buys the property and rents it to the borrower for a fixed period, with regular payments. At the end of the contract, the borrower can buy the property at an agreed price or return it to the bank.
Islamic insurance (takaful)
Islamic insurance, also known as the name of Takaful, are insurance products that comply with the principles of Islamic finance. Unlike conventional insurance, which is based on the concept of transferring risk to an insurance company, Islamic insurance is based on principles of mutual cooperation and risk sharing.
In Islamic insurance, participants contribute to a common fund to cover risks collectively. When a participant suffers loss or damage, they are eligible for financial compensation from this fund.
So, instead of paying insurance premiums, participants make contributions into a pool that is used to compensate claims.
🎓 Closing
Islamic banks are financial institutions that respect the principles of Islamic finance, based in particular on the prohibition of collecting or paying interest (ribâ). Booming, they now represent almost 2 billion dollars of assets around the world. But what are the specificities of their model compared to conventional finance?
First of all, Islamic banks apply the principle of profit and loss sharing. Rather than lending money in exchange for a fixed interest rate, they invest directly in economic projects and share the results, positive or negative, of these investments with their clients.
They also focus on activities that they consider it ethical. Games of chance, the sale of alcohol or weapons, pornographic sites, among others, are prohibited. The idea is to only finance projects contributing to the common good.
Finally, Islamic banks pay a portion of the profits they make to charitable associations, in the form of legal alms. called zakah. This tax specific to Islam is part of their DNA.
Behind these particularities lies a finance based on sharing, ethics and philanthropy. But what are the concrete implications of this alternative model? This is what we will see in the rest of this article.


















Leave comments